Overview

Have you ever wondered how you get connected to the world? How can you send your picture to the other side of the world? What is the internet and how it works?
The Internet can be said as a global wide area network that connects computer systems across the world. It includes several high-bandwidth data lines that comprise the Internet “backbone.” These lines are connected to major Internet hubs that distribute data to other locations, such as web servers and ISPs.
Though the internet was born in the 1960s, it was only in the 1990s when the potential of the internet to serve business was discovered, which then led to more innovation in this field.
There’s a excellent explanation of How does the internet work? This will clear many doubts about how you get a picture on your mobile sent from another corner of the world.
The next question you will ask is what about servers? Who manages it? Where are they installed? Ok..many questions but let’s not get distracted and break our questions into sub-questions and get clarified one by one. Let’s dive in then!
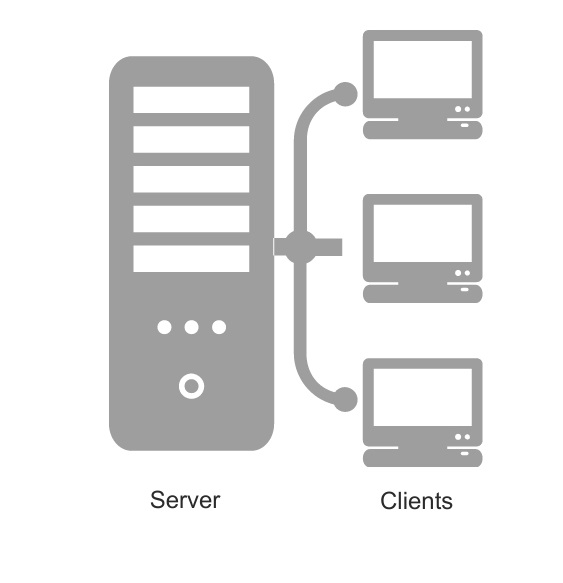
A client is a computer connected to the web. Like your laptop, mobile phone, television can be said as client.
A server is also a computer or system that provides resources, data, services, or programs to the clients over a network. In theory, whenever computers share resources with client machines they are considered servers.
Servers are made up of several different components and subcomponents. At the hardware level, servers are typically made up of a rack mount chassis containing a power supply, a system board, one or more CPUs, memory, storage, a network interface, and a power supply.
A data center comprises numerous key components, such as different types of servers, storage systems, switches, routers, and application delivery controllers. When installed and implemented properly, they provide computing resources, storage infrastructure, and network infrastructure that drive applications.
Now we are clear with a few definitions, let us see how the company manages it?
Back in the 90s, if the organizations’ needed to use the internet they would have to install many servers at their premises requiring huge allocated space separately. To maintain these data centers would require an altogether different department which is called as IT department. These IT departments would be responsible for procuring the servers, installing and maintaining them. There would be a security department for the safety of the servers because they house an organization’s most critical and proprietary assets, data centers are vital to the continuity of daily operations.
The upfront expense, maintenance costs, administration, and ongoing upkeep would incur a huge cost to these organizations. Trillions of dollars are spent worldwide on information technology, including hardware, software purchases, and application development.
And then, cloud computing comes to their rescue. Cloud computing refers to the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet.
Let us understand the differences between on-premises(servers under your control) with cloud(servers under control by third party) from the following table. So that, we can understand why cloud service demands are increasing year after year.
| Parameter | On Premise | Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Installation responsibility | The virtual machines including servers and all the associated components are running within the boundaries of the company. | The physical servers and all its associated components are managed by a third party cloud providers on an offshore location. |
| Operations | The businesses manage the data center and are responsible for maintaining it. | The organization directs all controls and IT management burden to the cloud providers. |
| Deployment of resources | Businesses need a robust IT infrastructure and a dedicated IT staff to manage everything. | The third party cloud providers are responsible for maintenance of the servers and their equipment inside the data centers. |
| Upfront Cost | The cost of running on premise data centers depends on the varying needs of the enterprise. | The cloud provider covers all the capital expenses including the cost of the equipment. Usage based billing. |
| Performance | Storage systems in close network proximity to application servers, users yield more predictable performance. | Poor internet connectivity impairs access and performance. |
Not surprisingly, much of the interest in cloud computing today is based on expectations of such cost savings. Cloud computing offers enterprise computing into a utility that can be accessed over the internet. Now, the best part is you don’t have to buy any server and maintain it, it all will be handled by the cloud provider which is running this application. Utility-based payment model reduced organization’s expenses and helped organizations to focus on developing various tools. This further enhanced software development productivity by the organizations.
If you are interested in learning more about how cloud technology came into existence and how it will shape the world, the book “The Big Switch: Rewiring the World, from Edison to Google ” by “Nicholas Carr”. The author has used an analogy of cloud computing with electricity is phenomenal and very easy to grasp the concepts around it.